
Ultimate Guide: Protect Sensitive Data with Watermarking
In today’s digital landscape, protecting sensitive data is more critical than ever. From confidential business reports to creative works like images and videos, unauthorized access and distribution pose significant risks. Watermarking is one of the most effective methods for safeguarding sensitive information. It helps prevent unauthorized use, spreads awareness, and enables tracking of leaks or intellectual property theft.
This guide explores everything you need to know about protecting sensitive data with watermarking, including how it works, its types, and the best tools
1. What is Watermarking?
Watermarking is a data protection technique that displays visible, customizable identifiers, such as user names, email addresses, IP addresses, timestamps, or session IDs, over digital or physical assets. These identifiers serve as persistent markers that indicate ownership, deter unauthorized use, and ensure the integrity of sensitive information.
Watermarking can be applied to a range of assets, including:
- Documents (PDFs, Word files)
- Images and videos
- Printed materials
- Application interfaces
- Live desktop sessions (screen watermarking)
Types of information that can be embedded in a watermark:
- User names or email addresses to tie content to specific users
- Timestamps to indicate when the content was accessed or viewed
- IP addresses or geolocation for tracing access origin
- Session IDs to track active sessions in real time
- Custom messages such as “Confidential,” “Do Not Share,” or policy reminders
2. Why Use Watermarking for Data Protection?
Screen Watermark is crucial in securing sensitive data in various industries like governmental entities, the Banking sector, and Healthcare organizations. Basically, every organization that handles sensitive data.
2.1 Key Benefits of Watermarking
✅ Prevents Unauthorized Distribution – Protects confidential data from being leaked.
✅ Authenticates Ownership & Copyright – Proves intellectual property rights.
✅ Tracks Information Leaks – Watermarks help trace data breaches.
✅ Maintains Data Integrity – Ensures digital files have not been altered.
✅ Deters Insider Threats – Employees are less likely to leak files when traceable watermarks are present.
3. Types of Watermarking & How They Work
There are various types of watermarking, each suited for different use cases.
🔹 Screen Watermark
The Screen Watermark embeds customizable watermarks at the OS level, displaying on all desktop screens. These watermarks show user identity, IP address, timestamps, and other metadata, reinforcing accountability and discouraging unauthorized sharing.
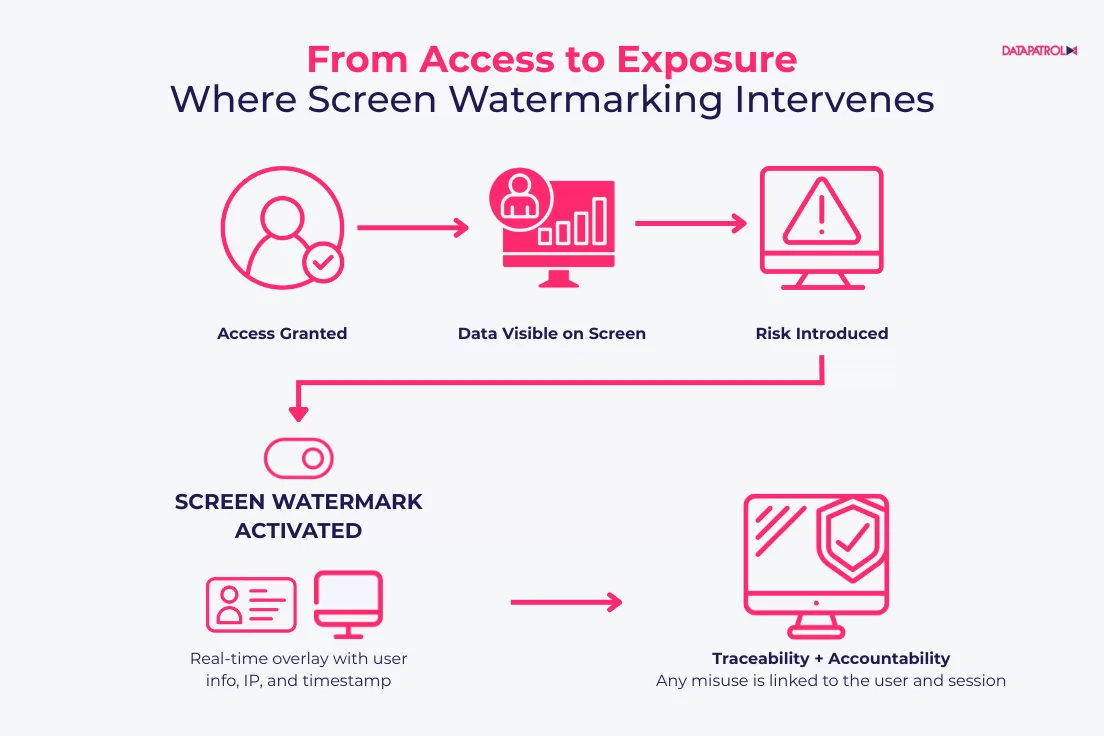
- Text Watermark:
Administrators can configure policies to display specific static or dynamic text on the screen. This text can include various types of metadata, which can be retrieved from the machine itself or Active Directory if integration is enabled. This feature’s flexibility allows for tailored and meaningful watermarks - Image Watermark:
The Image Watermark feature enables administrators to upload and customize an image that appears as a watermark on user screens. Key customization options include selecting the image’s size, transparency, and positioning. Organizations can use their company logo, QR codes, or other branding elements to enhance security while maintaining professionalism - Sliding Watermark:
The Sliding Text Watermark allows administrators to configure specific, static, or dynamic text that moves across the screen to a designated position. This feature supports customization options such as speed, position, color, and other display settings for the sliding watermark. Its dynamic nature ensures high visibility and adaptability to various scenarios
🔹 Printing Watermark
The printing watermark feature alters all printed documents to have a dynamic watermark containing user data. This can be applied to any printed document whether printed via a physical printer or into a PDF/XPS document.
🔹 WebMark
An SDK, a custom embeded watermark directly into a website or online portal with additional software required. By displaying visible identifiers such as user details, timestamps, and session data, this solution prevents unauthorized sharing and leakage of confidential information.
🔹 MobileMark
MobileMark is an advanced Android app that embeds a persistent watermark on device screens. This ensures security and constant oversight. The watermark remains visible to protect sensitive data regardless of the activity or application.
4. Watermarking Types Explained: Text, Image and Sliding
Watermarking typically comes in three main types, each designed for different environments, levels of visibility, and customization needs. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
Feature | Text Watermark | Image Watermark | Sliding Watermark |
Content Type | Text (static or dynamic) | Custom image (logo, QR code, etc.) | Moving text (static or dynamic) |
Customization | Metadata retrieval, font, size, position | Size, transparency, position | Speed, position, color, motion direction |
Visibility | Static on screen | Static on screen | Moves across the screen |
Integration | Active Directory metadata support | Upload custom images | Customizable movement and text |
Use Case | Ownership identification, session tracking | Branding, security reinforcement | High visibility, prevents screen capture |
5. Real-World Use Cases for Watermarking Solutions
Watermarking is used across several industries to ensure accountability, trace unauthorized access, and prevent data leaks, whether on-screen, in documents, or across mobile and web platforms.
🔍 Case 1: Tracing a Leaked Legal Report
A company embeds watermarks on their Portal that has legal documents. If a report leaks online, the watermark allows investigators to trace it back to the original recipient.
🔍 Case 2: Remote Access Control
A financial firm uses screen watermarks during remote sessions. Visible user details discourage screenshots and support audit trails.
🔍 Case 3: Medical Record Protection
A healthcare provider watermarks on-screen and printed records. In case of a leak, the watermark identifies the staff member involved.
6. Compliance & Data Protection Regulations
Watermarking plays an important role in helping organizations meet data protection and compliance requirements. By overlaying user-specific information on screen activity, it adds traceability and accountability, two key elements required by many regulatory frameworks.

Common Regulations Addressed by Watermarking:
- GDPR: Provides control and monitoring of sensitive personal data.
- HIPAA: Helps protect electronic health records and identify access points.
- PCI-DSS: Supports security requirements for environments handling cardholder data.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Adds a visible control layer to support information security best practices.
- NCA regulations (KSA): Aligns with Saudi Arabia’s cybersecurity compliance mandates for government and financial sectors.
Compliance Benefits of Screen Watermarking:
- Deterrence of intentional data leaks
- Proof of user accountability
- Session traceability for audits
- Compliance documentation and policy support
5. Industry Applications of Watermarking
Watermarking is used across industries where securing sensitive data, staying compliant, or protecting intellectual property is a priority. Here’s how key sectors apply watermarking to reinforce control and accountability:
🏦 Finance & Banking: Protects client data, transaction records, and internal reports.
🏥 Healthcare: Safeguards patient records by adding traceable identifiers on both digital screens and printed medical documents.
🎓 Education: Used to protect academic documents, exam papers, and internal communications.
🏛️ Government: Supports the secure handling of classified data by marking access points and preventing unauthorized sharing.
7. Best Practices for Watermarking Implementation
Watermarking is most effective when implemented thoughtfully across your environment. From choosing the right content to balancing visibility and usability, these best practices help organizations maximize security impact while maintaining a seamless user experience. 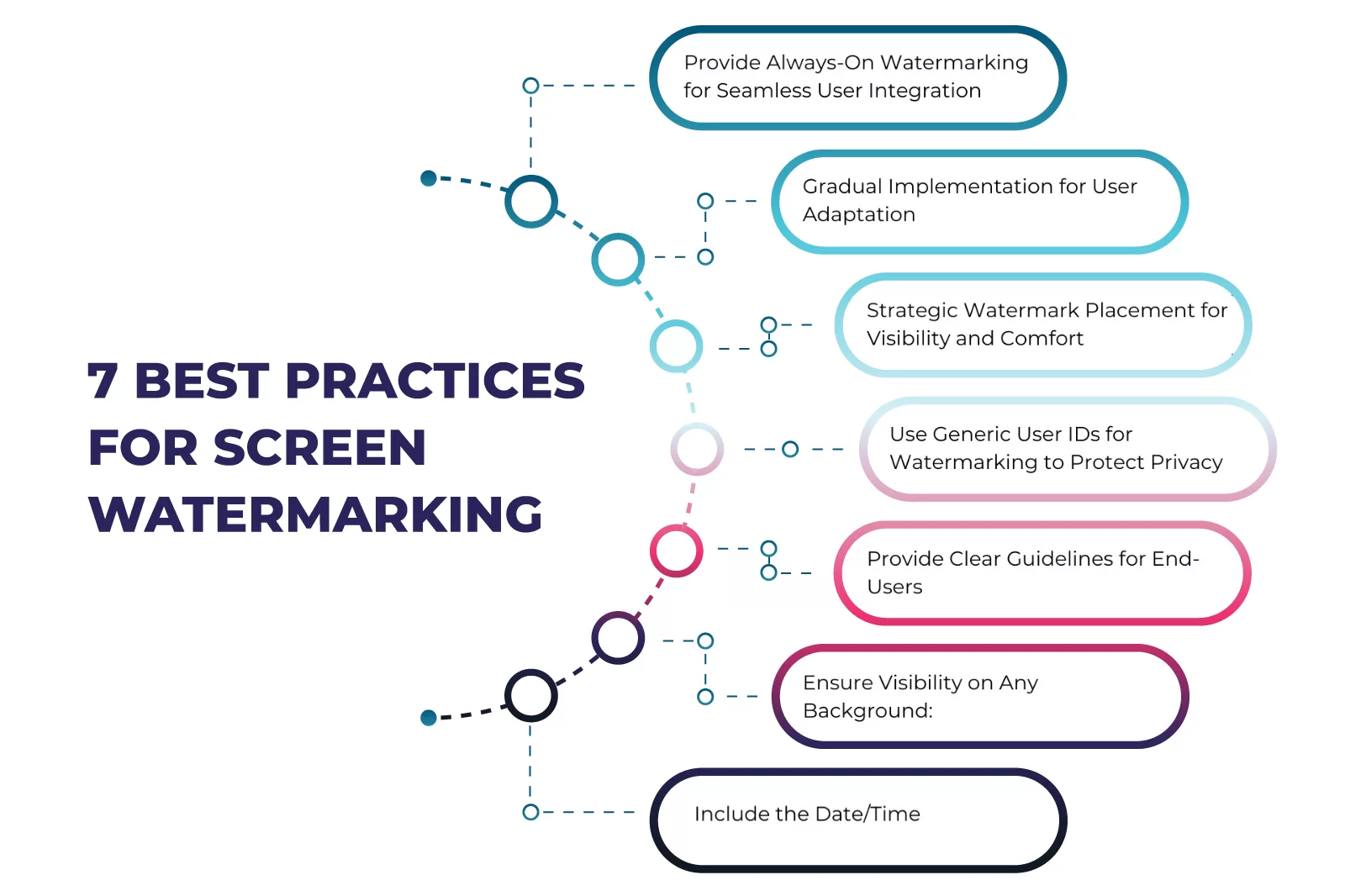
Conclusion
Watermarking is a powerful data protection tool that helps prevent unauthorized use, secure intellectual property, and track digital assets. Businesses and individuals can strengthen their cybersecurity measures by security their screens








