
Insider Threat Management: From Awareness to Prevention
Trusted employees, contractors, partners, and anyone with legitimate access to internal systems can pose an insider threat. And trust is what makes them one of the most dangerous cybersecurity risks. Whether intentional or accidental, insider incidents can result in data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
What are insider threats?
Insider threats refer to security risks that arise from individuals within an organization who have access to sensitive data, systems, or networks. These individuals can exploit their access maliciously or unintentionally, resulting in security breaches, data leaks, or operational disruption. The challenge with insider threats lies in their invisibility, making them one of the hardest and most challenging security risks to detect and monitor.
Types of insider threats

Understanding the different types of insider threats is essential for building a targeted response strategy:
- Malicious insiders: Employees or contractors who intentionally cause harm, often driven by revenge, financial gain, or ideology.
- Negligent insiders: employees who make mistakes, like misconfiguring systems, clicking phishing links, or using weak passwords.
- Compromised insiders: Individuals whose accounts or devices have been stolen by external actors, effectively turning them into unintentional threats.
- Third-party insiders: Vendors or partners with access to internal systems who may inadvertently or intentionally cause security incidents.
Identifying insider threats
Traditional security tools often fall short when it comes to detecting insider threats. Most systems rely on predefined criteria and static detection methods, which can be easily bypassed by individuals familiar with the organization’s internal processes, configurations, and controls.
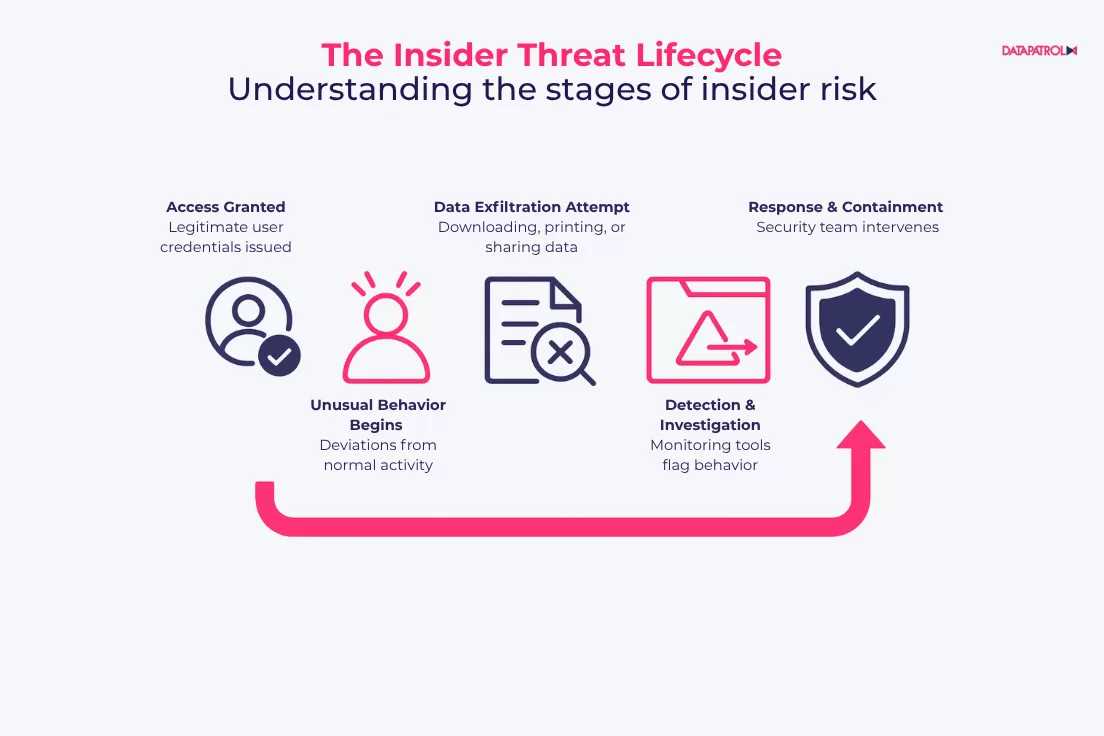
To effectively identify insider threats, organizations should focus on analyzing and detecting behavioral anomalies such as:
- Accessing sensitive systems or files at irregular hours or from unusual locations
- Downloading or transferring large volumes of data without a clear justification
- Attempting to access systems, tools, or documents outside the scope of one’s role
- Using unauthorized personal devices or external storage
- Repeatedly triggering security alerts or attempting to disable monitoring tools
In addition to monitoring user behavior, it is equally important to detect technical indicators that may signal an insider threat, including:
- Installing unauthorized software
- The presence of backdoors within the organization’s security infrastructure
- Disabling endpoint protections or tampering with audit trails
- Unusual combinations of access requests
By combining behavioral analysis with contextual awareness, organizations can improve their ability to detect, investigate, and respond to insider threats, minimizing potential damage before it escalates into a serious incident.
Why a Proactive Approach Is Necessary
Detecting insider threats is only the first step. Without a proactive strategy to manage risks and enforce response protocols, organizations will remain vulnerable to damage caused by overlooked or delayed actions. Insider incidents often develop over time through quiet policy violations, unnoticed data access, or gradually escalating behaviors.
This is why insider threat management must go beyond detection. It requires coordinated policies, real-time intervention capabilities, forensic abilities, and a framework that aligns security teams, HR, and legal departments to act decisively when warning signs appear.
What is Insider Threat Management?
Insider Threat Management (ITM) is a structured approach to identifying, mitigating, and preventing internal security threats. It involves a combination of policies, training, monitoring tools, and incident response processes. ITM is not a one-time initiative, it is an ongoing cycle of risk assessment, awareness building, and enforcement to protect sensitive information and ensure business continuity.
An effective ITM strategy includes:
- Risk profiling and access control
- Behavioral analytics and continuous monitoring
- Incident response planning and investigation capabilities
- Integration with broader governance and compliance frameworks (for example, ISO 27001, NIST CSF)
Awareness, the first layer against insider threats
Raising awareness is the first step in managing insider threats. Many incidents originate from negligence or a lack of understanding rather than malicious intent. Regular training, clear policies, and a culture of accountability help employees recognize risky behaviors, understand security protocols, and respond appropriately to suspicious activity. An informed workforce acts as a proactive line of defense and a human shield, reducing the likelihood of accidental or intentional harm from within.
Insider Threat Prevention Best Practices
Prevention is most effective when it’s layered, combining people, processes, and technology. Key practices include:
- Enforcing least privilege access: Ensure users only access the information necessary for their roles.
- Implementing continuous monitoring: Use tools to track user behavior, access patterns, and data movement.
- Deploying effective technologies to close data security gaps:
- Watermarking Solutions: A visual layer of protection that discourages data leaks by identifying users on screens, internal portals, and platforms, or shared files.
- Printing Watermarking: Marks sensitive documents with traceable identifiers.
- Anti-Copy and Print Screen Protection: Blocks common methods of internal data exfiltration, including copy-paste and print screen attempts.
- Conducting regular audits and risk assessments: Identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
- Establishing a clear incident response plan: Ensure the organization can act quickly and effectively when an insider threat is detected.
Building a Resilient Insider Threat Defense
Insider threat management is not just an IT responsibility, it’s a company-wide commitment. By combining technology solutions with employee awareness, access governance, and proactive monitoring, organizations can reduce the risk of insider incidents and respond effectively when they occur.
As insider threats continue to evolve, businesses must remain vigilant, adaptive, and strategic in their defense. Investing in the right tools, like DataPatrol’s Insider Threat Management Suite, and fostering a security-first culture will ensure long-term protection and operational resilience.








